Hardware User Guide
AD-CELLPACKBM-SL
System Setup
This section describes the procedure for establishing hardware connection between the boards, how to download the system requirements such as the firmware and software, and eventually obtain and view BMS readings through the Broad Market BMS graphical user interface.
Equipment Needed
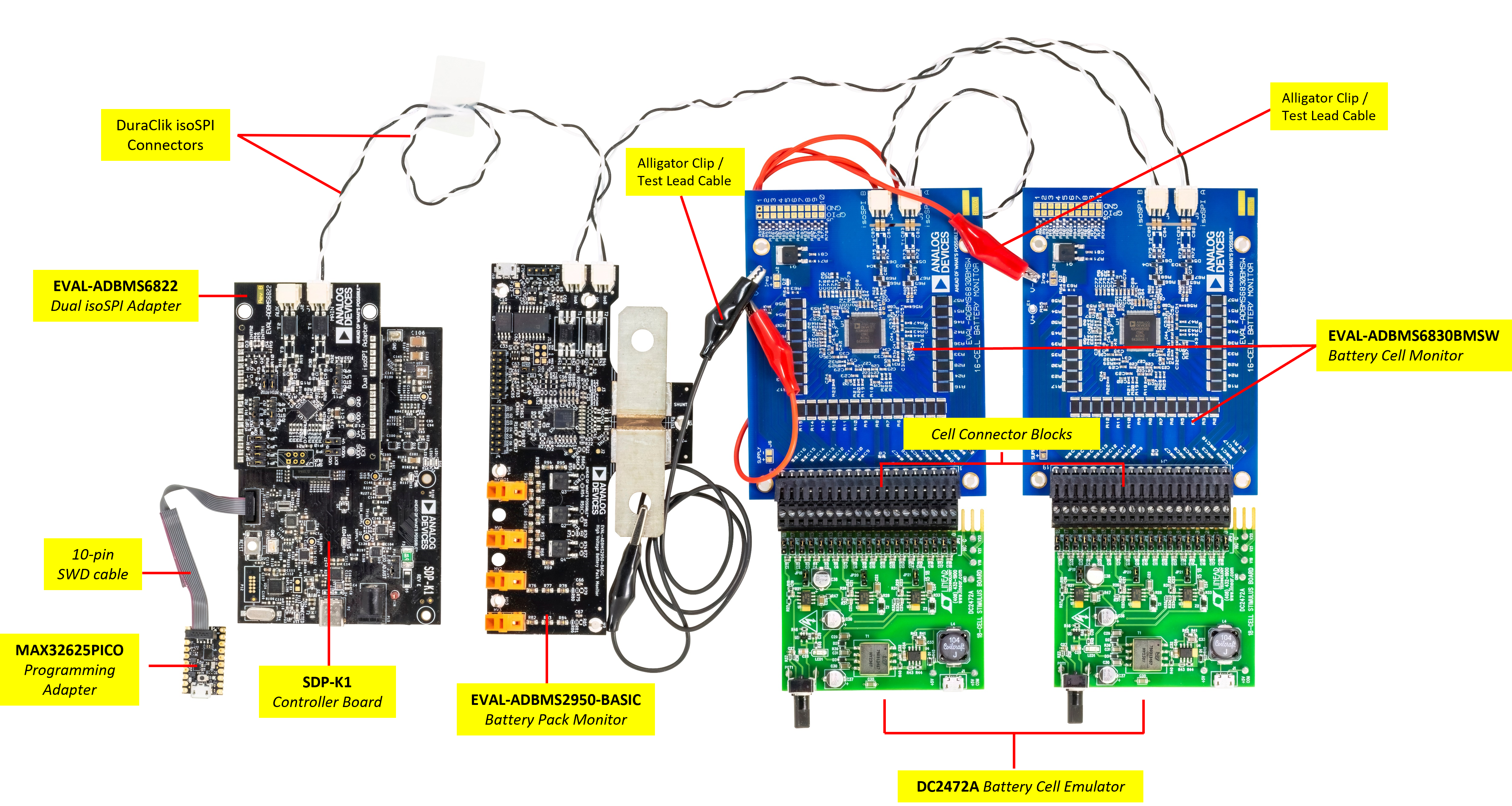
For easy identification of the components included in the kit, refer to the figure below.
Boards
2x EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW 16-Channel Battery Cell Monitor
1x EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC Battery Pack Monitor
1x EVAL-ADBMS6822 Dual isoSPI Adapter
1x EVAL-SDP-CK1Z (SDP-K1) Controller Board
2x DC2472A Battery Cell Emulator
1x MAX32625PICO Programming Adapter with 10-pin SWD cable (loaded with firmware image)
Cables and Other Accessories
2x Cell Connector Block (18-cell connector)
3x DuraClik isoSPI Twisted Pair Cables
3x USB Type A to Micro-B Cable
2x 12.0“ Alligator Clip / Test Lead, Black
1x 12.0” Alligator Clip / Test Lead, Red
1x 24.0“ Alligator Clip / Test Lead, Red
The following list of equipment are not provided as part of the kit, but are required for running the setup described in this guide.
Laptop or PC running Windows 10
Digital power supply (such as the Keysight e3631A 0V to 6V power supply)
2x wall plugs (to plug USB cable from DC2472A to provide power)
Software
The BMS Browser GUI is a PC browser based Graphical User Interface (GUI) tool designed to work in conjunction with the hardware in the AD-CELLPACKBM-SL. MyAnalog.com account will be required to download the BMS Browser GUI from below link:
When software updates or new versions of the software are available an email notification will be sent to the email address associated with the MyAnalog account used to download the original software package.
MCU Configuration & Setup
Note
By default (upon purchase), the AD-CELLPACKBM-SL Kit comes with a MAX32625PICO programmer adapter that is already loaded with the appropriate firmware image. Otherwise, if you are using a new MAX32625PICO programmer (that is not part of the original kit), make sure to flash it first with the correct firmware image before using it with the AD-CELLPACKBM-SL BMS Kit. If you do not know how to load the image, follow the instructions below.
The MCU should be programmed using the following steps:
MAX326825PICO Debugger (One-time setup)
Download and install the BMS Browser GUI Broadmarket.
- Open the program files folder of the BMS Browser GUI in the host PC and look for the SDP-K1 .bin file.
C:\Analog Devices\BMS_Browser_GUI_Broadmarket-Rel2.0.0\USB_TO_SPI_Firmware
Plug the micro USB cable to the MAX32625PICO.
Press the button on the MAX32625PICO and then plug the other end of the micro-USB cable into the PC. A red LED should blink, then hold steady, and a MAINTENANCE drive should appear on your PC.
Drag and drop the
SDP_K1_PyBMS_USB_TO_SPI_Bytes_Debug_USB_Port.binfile onto the MAINTENANCE drive. The file transfer should be complete in about 30 seconds.Unplug and replug the device.
After completing this step, a DAPLINK drive should appear. You can drag and drop the firmware (.bin files separate from the above) onto it to program the SDP-K1.
BMS Browser GUI Installation
Download the BMS Browser GUI in your Host PC.
Double click on
bms_browser_gui_broadmarket-relX.Y.Z.exeto install the GUI.Accept the license terms and click Next` to proceed with the installation. The default installation directory will be in
C:\Analog Devices\.
Launching the BMS Browser GUI
Open the BMS Browser GUI either by searching for it in the Start Menu` or using the shortcut on the Desktop.
Run the application to launch the BMS Browser GUI.
Upon launching, a console window will appear to display background information.
Two new tabs will open in the default browser on the PC, with the User Guide tab as the default.
Switch to the alternative tab to access the BMS Browser configuration page, which should be displayed.
Ensure that the SDP-K1 is connected to the PC via the USB-C cable on P10. The Blue LED, D31 will illuminate when powered.
In the Serial Port dropdown box, select the COM port associated with SDP-K1.
Battery Cell Monitoring
Setup
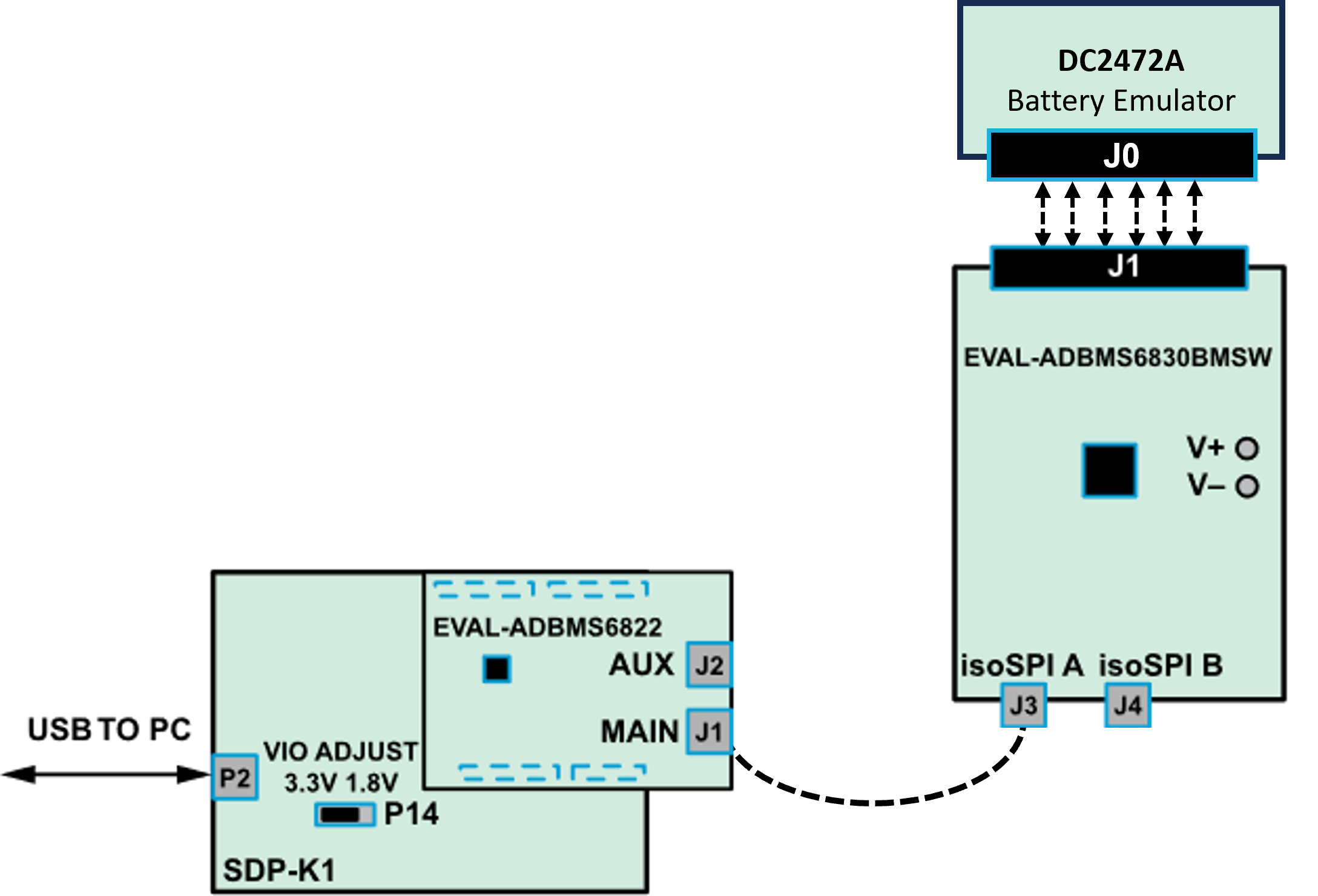
This setup uses the SDP-K1 as the controller board, but users may also use the AD-APARD32690-SL as MCU and follow the same hardware setup instructions.
The DC2472A Battery Emulator Board was also used for cell voltage input. Alternatively, resistors can be used to simulate battery cell voltages. 100 Ω ½ W or equivalent resistors are recommended because 100 Ω (or lower values) typically will not induce measurement errors, and the ½ W (or greater rating) will keep the resistor temperatures low, preventing power dissipation damage.
Check the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW User Guide for procedure on connecting resistors.
Connect the EVAL-ADBMS6822 dual isoSPI adapter to the EVAL-SDP-CK1Z (SDP-K1) controller board through the Arduino headers.
Set the P14 jumper of the SDP-K1 to the 3.3 V position.
Connect the SDP-K1 (P2) to the Host PC using a USB cable.
Connect the EVAL-ADBMS6822 (J1) to the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW (J3) using the 2-wire twisted-pair patch cable from the main DuraClik connector to isoSPI A DuraClik connector.
Plug the screw-terminal block(s) into the cell voltage connectors of the DC2472A battery emulator board. Note that the last three terminals of the DC2472A must be left hanging.
Connect the DC2472A battery emulator board to the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW through the connected cell voltage connectors (J1).
Power the DC2472A** using a 5 V external source connected to J1 using a USB cable. Alternatively, power it through PC using a USB cable to be connected via J10.
While some laptop USB ports may suffice for powering the emulator during evaluation, it is still recommended to use an external power supply to ensure adequate power. Note that the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW is powered through the DC2472A.
Attach the MAX32625PICO programmer to the SDP-K1 using the 10-pin ribbon SWD cable. Observe correct polarity when connecting the SWD cable.
Test
Open the BMS Browser GUI.
Go to the Interface Connection` section and select the COM port associated with the SDP-K1.
Under the Daisy Chain` section, ensure the Generation` dropdown box is set to ADBMSGEN6.
From the Products list, select the ADBMS6830, then click on the right arrow to add it to the Daisy Chain. Settings can remain as default.
Click Launch.
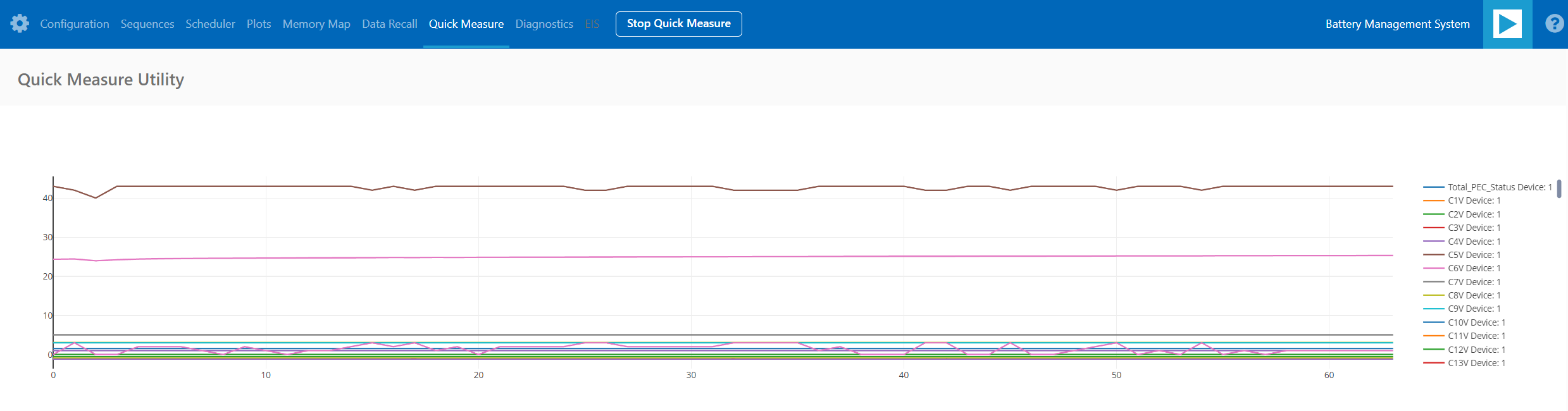
Upon launching, the Quick Measure` tab will open. Note: this utility only supports a single BMS product in a Daisy Chain. Click Start Quick Measure` to begin measurements.
Check the Total PEC Status` on the 3rd row under the Memory Map. This indicates the status of the isoSPI link between the EVAL-ADBMS6822 and the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW.
Ensure the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW board is powered correctly, indicated by the Blue LED on the DC2472A being illuminated.
Verify the connection of the twisted cable between the EVAL-ADBMS6822 and the EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW.
Check the voltage readings by adjusting the potentiometer (POT1) on the DC2472A to modify the emulated cell voltages. Monitor the voltage channels on the Quick Measure Utility graph. Select which signals to display on the graph under the Plot All Devices` column.
Battery Pack Monitoring
Setup
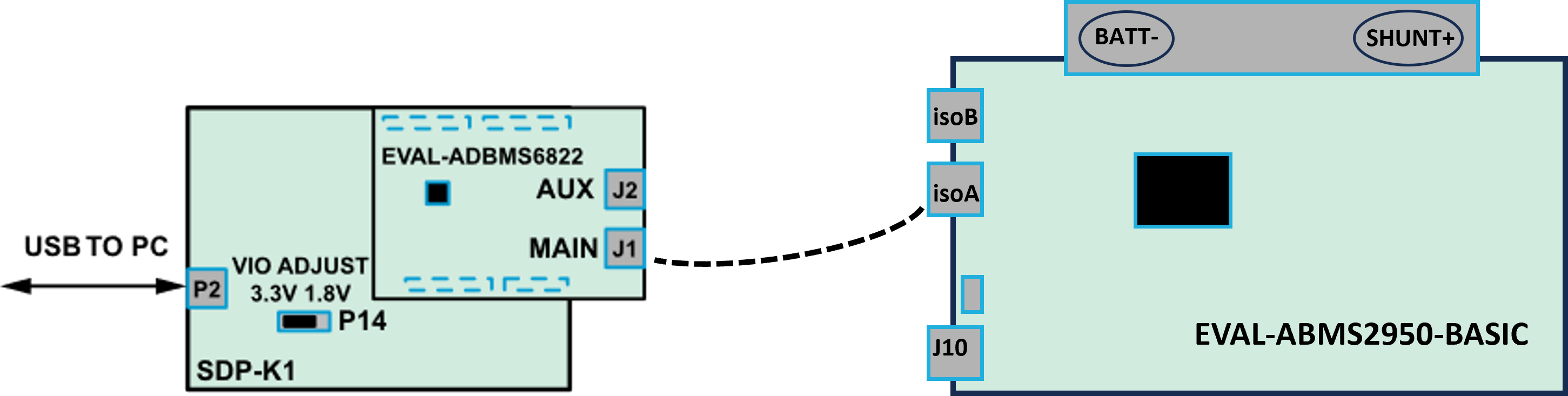
Connect the EVAL-ADBMS6822 dual isoSPI adapter to the EVAL-SDP-CK1Z (SDP-K1) controller board through the Arduino headers.
Set the P14 jumper of the SDP-K1 to the 3.3 V position.
Connect the EVAL-ADBMS6822 (J1) to the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC (isoA) using the provided isoSPI cable.
- Choose between two options for powering the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC:
Supply 5 V to J1 and set the current limit to 200 mA. The EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC consumes less than 50 mA in idle mode and ~100 mA in active mode.
Alternatively, power it using a micro-USB cable connected to J10.
Attach the MAX32625PICO programmer to the SDP-K1 using the 10-pin ribbon SWD cable. Observe correct polarity when connecting the SWD cable.
Connect one end of the USB cable to SDP-K1 (P2) and the other end to the host PC.
Test
Open the BMS Browser GUI.
Go to the Interface Connection` section and select the COM port associated with the SDP-K1.
Under the Daisy Chain` section, ensure the Generation` dropdown box is set to ADBMSGEN6.
From the Products list, select the ADBMS2950, then click on the right arrow to add it to the Daisy Chain. Settings can remain as default.
Click Launch.
Upon launching, the Quick Measure tab` will open. Note: it can only handle one BMS product in a Daisy Chain. Click Start Quick Measure` to begin measurements.
Check the Total PEC Status` on the Memory Map. It should reflect true, indicating a successful isoSPI link between the EVAL-ADBMS6822 and the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC. If false, there is an error in the signal chain.
Complete Daisy Chain
Setup
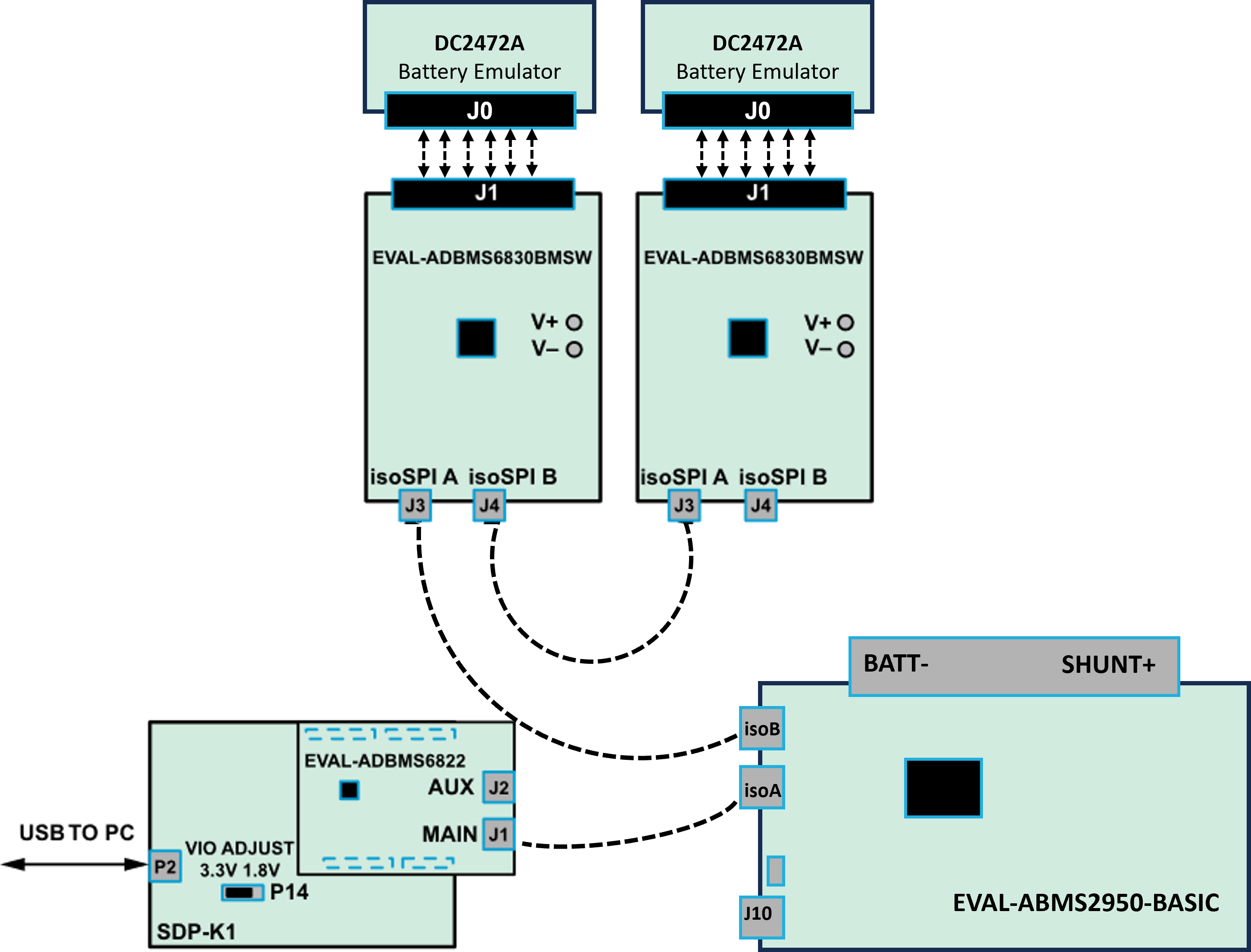
Once familiar with the setup for each of the individual boards the entire signal chain can be verified.
Connect the hardware using the DuraClik isoSPI cables, as shown in the diagram below.
Power each DC2472A battery emulator board using a 5 V external source connected to J1 through the USB cable.
Power the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC either through J1 or J10, as explained earlier.
Using the black alligator clip cable, connect the V- pin of the second EVAL-ABMS6830BMSW to the BATT- port of the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC.
Using the red alligator clip cable, connect the V- pin of the first EVAL-ABMS6830BMSW board to the V+ pin of the second EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW.
Attach the MAX32625PICO programmer to the SDP-K1 using the 10-pin ribbon SWD cable. Observe correct polarity when connecting the SWD cable.
Connect one end of the USB cable to SDP-K1 (P2) and the other end to the host PC.
Test
Launch the BMS Browser following the previous instructions and choose the appropriate COM port.
Set up the Daisy Chain according to the diagram provided. The EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC is positioned at the top, indicating it is the initial device on the chain, connected to the EVAL-ADBMS6822. The first EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW connects to the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC, while the second EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW is linked to the first one via the isoSPI cable.
Click on Launch to initiate the GUI. After the GUI launches in the Browser, go to the Sequences tab located in the top toolbar, which will open the Sequence Configuration page.
In the Files` column, select the ADBMS6830-ADBMS2950.json. This action will load a preconfigured sequence into the tool.
Click on Initialization Sequence` followed by General Initialization` under the Sequences` column to load the defined sequences from the ADBMS6830-ADBMS2950.json file into the tool.
Next, select Loop Sequence` and then click on General Readback Loop` under the Sequences column. This action loads the loop sequence defined in the ADBMS6830-ADBMS2950.json file into the tool.
Finally, click on Start Freerun` to initiate the freerun mode.
During free run mode, the Initialization Sequence` is performed once initially. Subsequently, the loop sequence continues to run continuously until the Stop Freerun button is clicked.
After activating freerun mode, navigate to the Memory Map` tab. This section displays a numerical representation of the ongoing command loop. Additional details can be accessed in the GUI’s help section. The accompanying screenshot illustrates this output.
The Plots` tab allows for the visualization of parameters recorded during the command loop. It supports the creation of up to four plots simultaneously.
Note
In the configured Daisy Chain, the EVAL-ADBMS2950-BASIC is designated as Device 1, the first EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW as Device 2, and the third EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW as Device 3. An example illustrates how to plot each parameter separately: I1ACC and I2ACC on Plot 1, the average cell voltages for the first EVAL-ADBMS6830MSW on Plot 2, and the averaged cell voltages for the third EVAL-ADBMS6830BMSW on Plot 3.
Simply choose the desired Plot number from the dropdown menu under each device to display the relevant data.
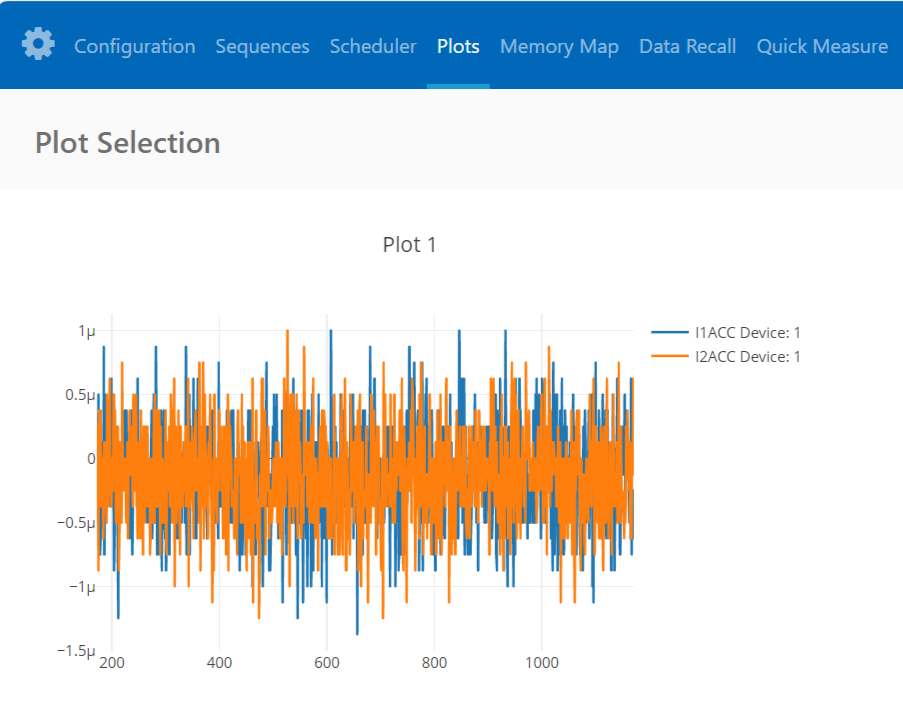
Plot settings can be saved to the PC to be reloaded for future session to save time.
Resources
Design & Integration Files
Download
AD-CELLPACKBM-SL Design Support Package
Schematic
PCB Layout
Bill of Materials
Allegro Project